Top 10 Biometric Entry Systems That Enhance Security Today?
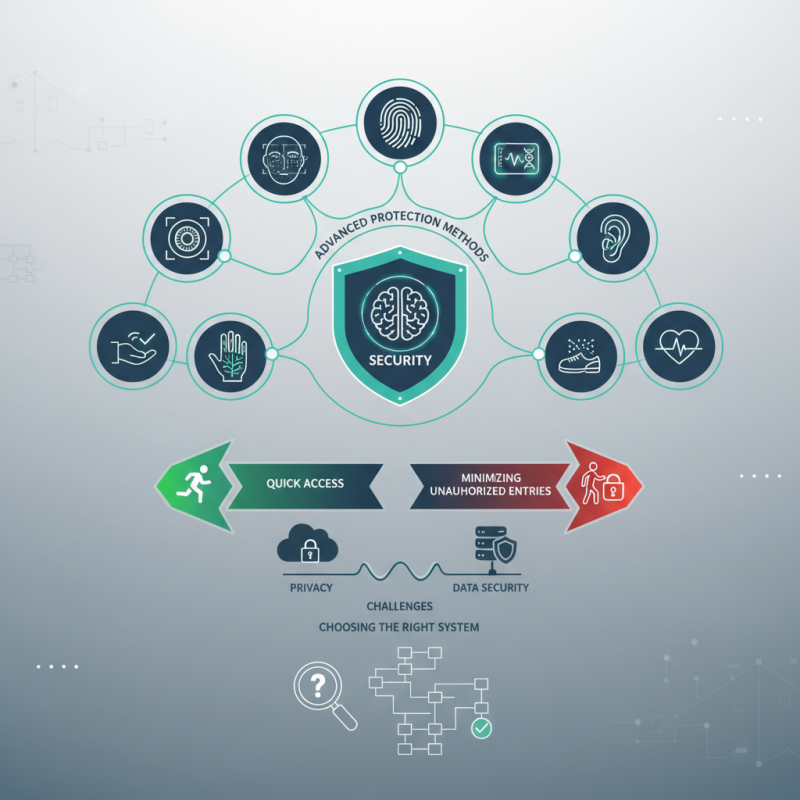
In today’s world, security is more important than ever. A Biometric Entry System offers advanced protection methods. These systems rely on unique biological characteristics. Fingerprints and facial recognition are popular examples. They tackle security challenges that traditional methods face.
The rise of technology amplifies the need for reliable entry systems. Many organizations choose biometric solutions to enhance security. These systems can provide quick access while minimizing unauthorized entries. However, implementing a Biometric Entry System is not without flaws. Concerns about privacy and data security persist. Organizations must navigate these issues carefully.
Choosing the right system is crucial. It requires careful consideration of specific needs. Not all biometric systems are equally effective. The variety can be overwhelming. Overall, the current landscape offers exciting, yet challenging, possibilities for security advancements through biometric technologies.
Overview of Biometric Entry Systems in Modern Security
Biometric entry systems are revolutionizing security in various sectors. These systems use unique physical characteristics for identification, making unauthorized access extremely difficult. Reports indicate that the global biometric market is projected to reach $60 billion by 2026, reflecting growing adoption in corporate environments, airports, and personal devices.
Fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans are common biometric methods. Each of these methods has its own advantages and limitations. For example, while fingerprint scanners are widely accepted, they can be susceptible to spoofing. Facial recognition offers rapid access but may not work well in varying light conditions. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective implementation.
Tip: Assess the environment before choosing a biometric system. Not all systems are suited for every situation.
As organizations adopt biometric systems, they must address privacy concerns. Users often worry about data breaches, which can undermine trust. In fact, a survey revealed that 30% of consumers fear sharing their biometric data. This highlights the need for transparent data policies and robust encryption methods.
Tip: Educate users about how their data is protected. This builds confidence in new technologies.
Types of Biometric Technologies Used in Security Solutions
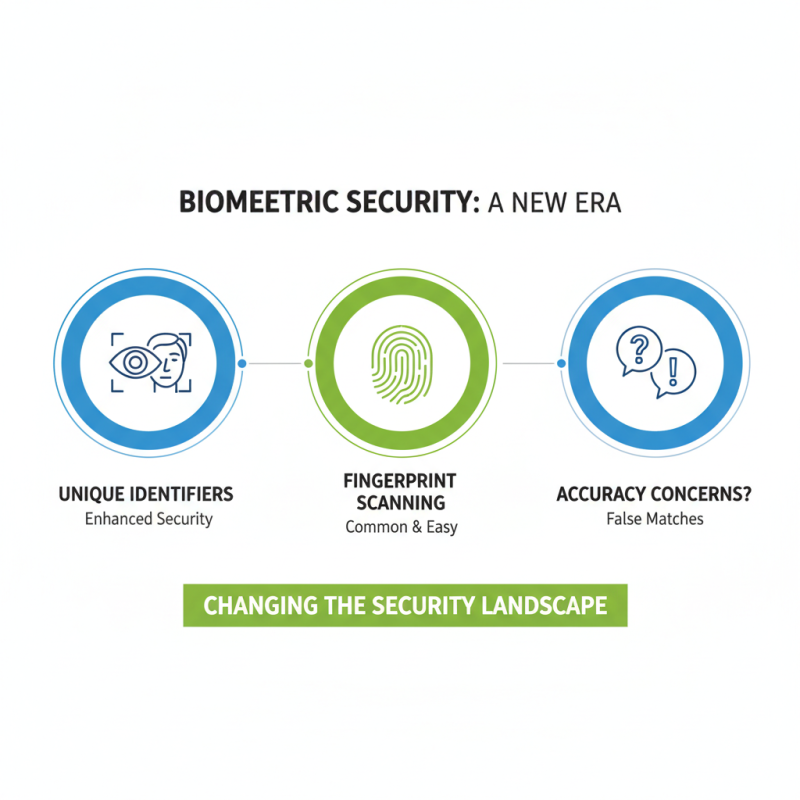
Biometric technologies are changing the security landscape. These systems improve safety with unique identifiers. Fingerprint scanning is one of the most common methods. It’s easy to use and widely accepted. However, you may worry about accuracy and false matches.
Face recognition technology is becoming more popular. It analyzes facial features to verify identity. While it’s effective, privacy concerns are valid. Many people feel uneasy about their images being stored.
I recommend you always review privacy policies. Ensure the data is handled responsibly. Keep in mind potential risks when using these systems. Retina scans provide another layer of security. They are accurate and difficult to replicate. Yet, the process can be slow, leading to frustration.
When choosing a biometric system, think about user experience. Balance security needs with convenience. Some users might struggle with newer technologies. The key is finding a system that works for everyone involved. Consider regular training or updates to improve familiarity.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing a Biometric System
When choosing a biometric entry system, several key features stand out.
Accuracy is paramount. A study by the
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) reveals that accuracy rates can vary
significantly among systems. Up to 20% of users may face false rejections or acceptances
in poor-performing systems. This statistic highlights the importance of selecting a reliable technology.
Integration capabilities are also
crucial. With 70% of organizations looking for compatibility with existing systems, seamless
integration reduces operational friction. Biometric systems should work harmoniously with access control
and surveillance solutions. Companies should not underestimate this aspect.
User-friendliness is another factor to consider. A complex interface can lead to operational errors. An
intuitive design enhances user experience and adoption rates. It's also essential to think about
privacy concerns. Balancing security with user
privacy can be challenging. Reports show that 30% of users are wary of biometric data
misuse. This apprehension must be addressed through transparent practices.
Top 10 Biometric Systems: Features and Benefits
Biometric entry systems have become a key solution for improving security. These systems use unique physical traits to grant access. Fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans are popular methods. They offer convenience and enhance safety for homes and businesses.
One major benefit of biometric systems is their accuracy. Unlike traditional keys, biological markers are hard to duplicate. However, these technologies can be prone to errors. For example, environmental factors may hinder a face recognition system’s performance. Sometimes, users find them frustrating if they aren't calibrated properly.
Another significant feature is the quick access capability. Biometric systems often provide faster entry than keypad locks. This advantage is crucial in emergency situations. Nevertheless, privacy concerns linger. Users must be aware of how their biometric data is stored and protected. Transparently addressing these concerns can enhance user trust and confidence.
Top 10 Biometric Entry Systems - Security Features Comparison
Real-World Applications of Biometric Entry Systems in Security
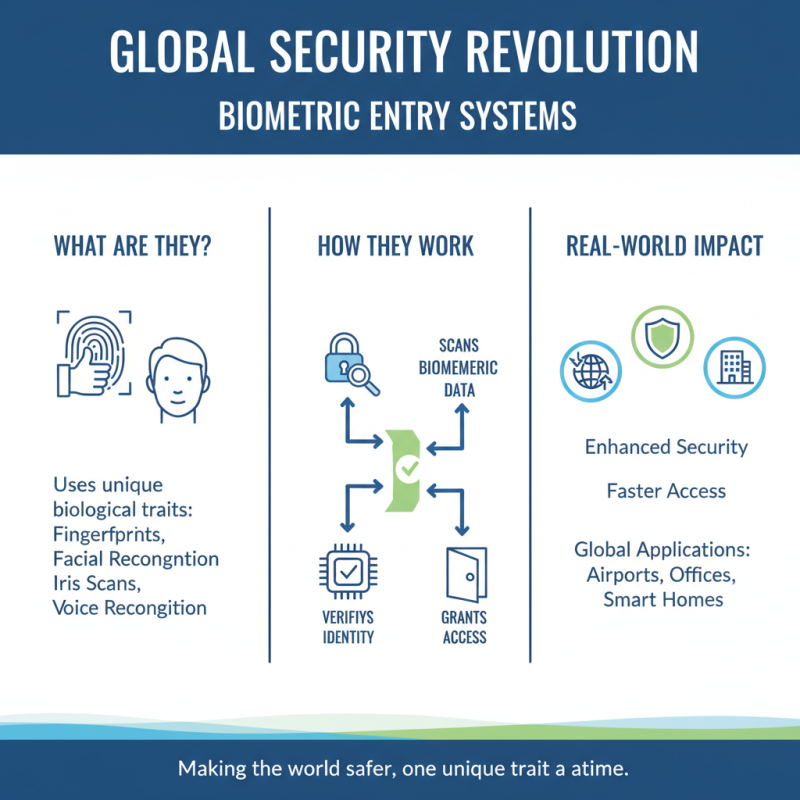
Biometric entry systems are changing security measures worldwide. These systems use unique biological traits, such as fingerprints and facial recognition, to grant access. Real-world applications show how effective they can be.
For instance, many offices now utilize fingerprint scanners. Employees place their fingers on the scanner, which quickly verifies their identity. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access. However, what happens when a system fails? Some employees may get locked out, highlighting a potential inconvenience. Regular maintenance can help avoid such issues.
In educational institutions, facial recognition is gaining popularity. Schools use it to track attendance and enhance security. Students simply walk through the entry points, and the system recognizes them. Still, concerns about privacy are looming. Schools must ensure a balance between security and students' rights.
Tips: Always keep biometric systems updated. Regular checks can catch glitches early. Consider having a backup access method, just in case. Enhance your staff training on these systems to minimize errors.
Related Posts
-

10 Unmatched Reasons Why the Best Biometric Device Revolutionizes Security Today
-

Unleashing Global Potential with the Best Fingerprint Machines Made in China
-

10 Compelling Reasons to Choose the Best Biometric Access Control for Your Business
-

Ultimate Checklist for Implementing a Biometric System in Your Business
-

Ultimate Guide to Implementing Biometric Entry Systems in Your Workplace
-

The Comprehensive Ultimate Guide to Biometric Security Solutions for Your Business