2026 Best Biometric Devices for Enhanced Security and Convenience?
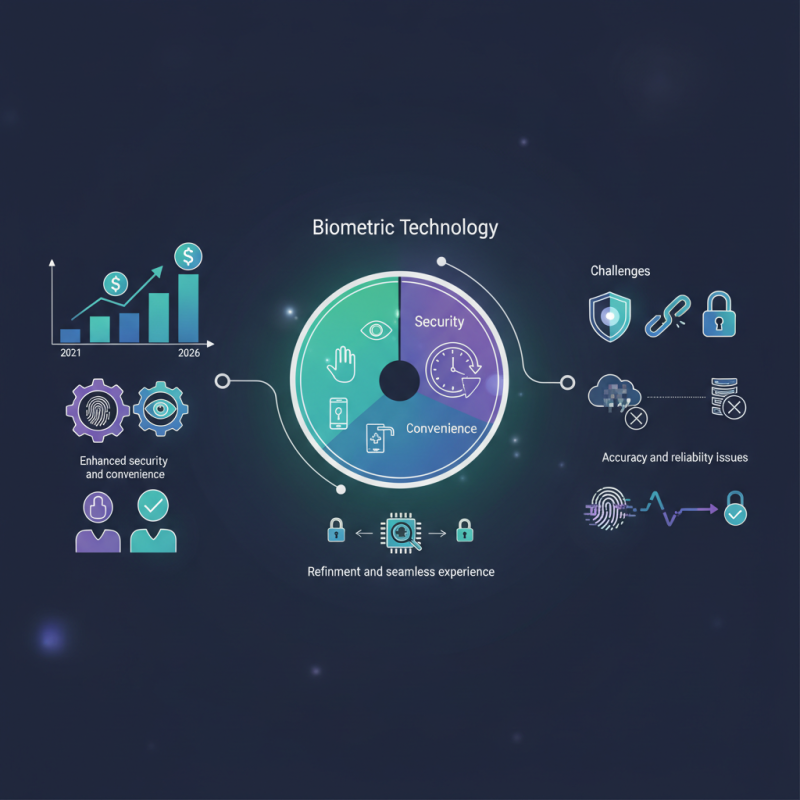
In recent years, the demand for biometric devices has surged significantly. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the biometric market is expected to grow from $28.65 billion in 2021 to $59.31 billion by 2026. This rapid growth highlights the increased focus on security and convenience in various sectors, including finance, healthcare, and personal devices.
Biometric devices, such as fingerprint scanners and facial recognition systems, offer quick access and enhanced security. A study by Grand View Research reveals that 55% of consumers prefer using biometric devices over traditional passwords. This shift indicates a stronger desire for user-friendly security solutions. However, the rise of these technologies also brings challenges. Data privacy concerns are at the forefront, as breaches can expose sensitive information.
Despite their benefits, not all biometric systems are foolproof. Some systems can struggle with accuracy under different conditions. This inconsistency raises questions about reliability. As the industry evolves, it's crucial to address these imperfections. Developers must focus on refining technology to ensure a seamless user experience, enhancing both security and convenience.
2026 Overview of Biometric Technologies in Security Solutions
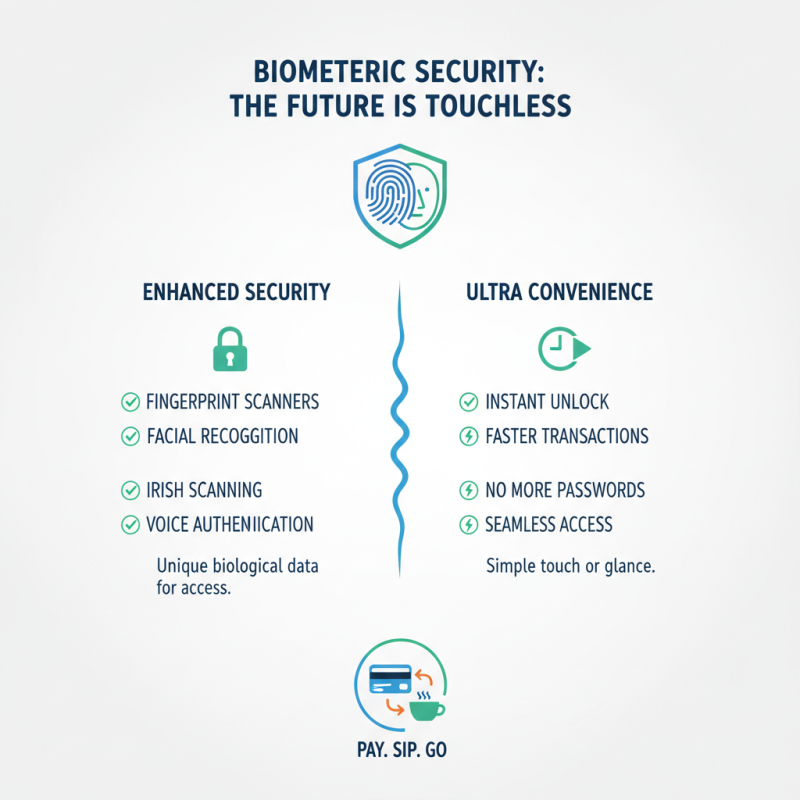
Biometric technologies are becoming increasingly vital in today's security solutions. Fingerprint, face, and iris recognition systems are now commonly used. These methods provide quick access and are difficult to replicate. For example, a simple touch or glance can unlock devices. However, concerns about privacy and data security arise. How can we ensure that our biometric data is safe?
As more businesses adopt biometrics, the challenge lies in balancing convenience and safety. Misuse of biometric data can have severe consequences. If systems are hacked, personal information may be exposed. This realization prompts a need for robust encryption and security measures. Continuous advancements in technology may help address these flaws, but skepticism still exists.
Moreover, the user experience must not be overlooked. Frustrating systems can lead to resistance and low adoption rates. If the technology fails in real-world situations, trust will diminish. A well-designed biometric solution should be seamless and user-friendly. The future of security depends on innovation and addressing these valid concerns.
2026 Best Biometric Devices for Enhanced Security and Convenience
This chart showcases the percentage usage of various biometric technologies in security solutions as of 2026, highlighting trends towards enhanced security and user convenience.
Key Biometric Devices: Trends and Adoption Rates in 2026
In 2026, the landscape of biometric devices is evolving rapidly. Users now prioritize security and convenience. Fingerprint scanners remain popular, but facial recognition is gaining ground. These technologies are becoming more affordable and user-friendly.
Adoption rates are rising steadily. Many businesses are integrating biometrics into their operations. Accessing secure areas, logging into systems, or even making payments is seamless. However, concerns about privacy and data security persist. Not everyone is comfortable with storing biometric data. There is a growing demand for transparency in how this information is used.
Real-world applications showcase both successes and challenges. Some organizations experience smoother operations, while others face technical glitches. Users must weigh convenience against potential risks. Balancing security and user experience is crucial. The future of biometrics is promising, but it requires continuous reflection and adjustment.
2026 Best Biometric Devices for Enhanced Security and Convenience
| Device Type | Adoption Rate (%) | Key Features | Market Segment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fingerprint Scanner | 75 | Fast authentication, compact design | Personal Devices |
| Facial Recognition | 68 | Convenient, hands-free operation | Security Systems |
| Iris Scanner | 60 | High accuracy, secure | High-Security Facilities |
| Voice Recognition | 45 | User-friendly, remote access | Smart Devices |
| Palm Print Scanner | 35 | Large capture area, secure | Research and Development |
Comparative Analysis of Fingerprint, Facial, and Iris Recognition Technologies
Biometric technology has gained immense popularity for enhancing security and user convenience. This analysis focuses on three primary methods: fingerprint, facial, and iris recognition. Each method has its unique features and drawbacks, making it crucial to examine them closely.
Fingerprint recognition offers ease of use. It requires only a scan of the finger. However, it is not foolproof. Some individuals have issues with dry skin or scars that may prevent accurate readings. Furthermore, fingerprints can be replicated under certain conditions, raising security concerns.
Facial recognition technology is widely adopted due to its quick processing speed. It captures facial features and analyzes them against stored data. Yet, it's susceptible to errors in low light or crowded environments. Privacy concerns also loom large as people grapple with surveillance implications.
Iris recognition stands out for its high accuracy. The unique patterns of the iris make it difficult to forge. However, it can be inconvenient for users who wear glasses. Additionally, this method often requires specialized equipment that may not be readily available. All these factors highlight the nuances in choosing the right biometric technology for security needs.
Impact of Biometric Security on Fraud Reduction and User Convenience
Biometric security is revolutionizing how we protect our personal information. Fingerprint scanners and facial recognition systems are becoming standard. They offer more than just security; they enhance user convenience. With a simple touch or glance, users can access their devices and accounts. This speed makes transactions easier. Imagine buying coffee without fumbling for your wallet or phone.
Despite the benefits, there are valid concerns. Biometric data is sensitive. If compromised, it cannot be easily changed like a password. Users must consider potential data breaches. A single database leak can expose thousands. Trust in these systems relies on robust security measures. Many still worry about privacy and misuse of their biometrics.
Fraud reduction is a significant advantage. Traditional passwords can be stolen or guessed. Biometric methods are harder to replicate. Thieves may find hacking a fingerprint challenging. This feature builds trust between users and service providers. However, users should remain vigilant. Continuous improvement is necessary to address evolving threats. The journey of biometric security is complex, but it holds great promise for the future.
Future Innovations in Biometric Devices: Predictions and Potential Challenges

As we look towards 2026, biometric devices continue to gain traction. Innovations promise enhanced security and convenience. However, they're not without challenges. Many users may struggle with privacy concerns. How much data are we willing to share?
Emerging technologies, such as advanced facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, offer speed and ease. Yet, mistakes can happen. A device may misidentify a user, leading to unauthorized access. The importance of accuracy cannot be overstated. Developers face the constant pressure to improve upon existing flaws.
Additionally, the potential for hacking raises alarms. Cybersecurity threats evolve rapidly. The robustness of biometric systems must keep pace. As these technologies advance, society must tread carefully. Balancing innovation with security and ethical considerations is crucial. The journey ahead will be complex and thought-provoking.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking Security and Convenience with the Best Biometric Device Advantages
-

How to Choose the Right Biometric Device for Your Business Security Needs
-

10 Unmatched Reasons Why the Best Biometric Device Revolutionizes Security Today
-

Exploring Innovative Alternatives to the Best Biometric Device for Global Buyers
-

10 Reasons Why Biometric Attendance Machines Stand Out as the Best Choice for Modern Offices
-

Ultimate Checklist for Implementing a Biometric System in Your Business